
Ford’s latest On Target includes information on new technologies, SRS
By onAnnouncements | Business Practices | Collision Repair
Ford shared information related to new safety technology, a side-impact door sensor and its supplemental restraint system (SRS) in its latest On Target newsletter.
Its 2023 F150 adaptive energy absorbing steering column will collapse if an air bag deploys and drop down to protect the driver, which is a consideration worth noting for repairers tasked with fixing them following a collision.
The OEM’s workshop manual for that MY pickup, notes that “precise tolerances are required when manufacturing a steering column.”
“Never install a repaired, rebuilt or remanufactured steering column, always install a new steering column,” the manual says. “Failure to follow this direction can result in steering column failure.”
In its latest On Target newsletter, the OEM said its adaptive energy absorption steering column, which can be found on the F-150, includes a device that when deployed reduces the amount of force necessary to collapse the steering column during a collision.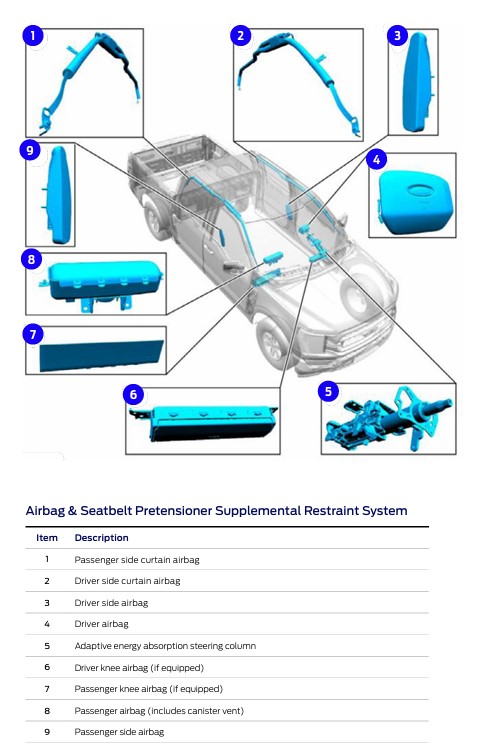
“The deployable device is activated by the restraints control module (RCM), depending on the driver seat position and the force of the crash,” On Target said. “After deployment, a new steering column must be installed.”
It added that after a vehicle has been in a crash, repairers should inspect the restraints control module and impact sensor mounting area for any damage or deformation. It should inspect related components for cracks damages or loose fasteners as well, it said.
If the mounting is damaged, On Target said repair professionals should restore the areas to their original configuration. After doing so, it said the RCM and impact sensors in the area should also be compiled with a new component, even if the air bag was not deployed.
“Failure to follow these instructions may result in serious personal injury or death in a subsequent collision,” it said.
Collision repair facilities should always refer to the appropriate workshop manual procedure before completing vehicle repairs that affect the SRS and seatbelt system, On Target said.
“The SRS must be fully operational and free of faults before the vehicle can be released to the customer. Precise tolerances are required when manufacturing a steering column,” it said. “NEVER install a repaired, rebuilt or remanufactured steering column. ALWAYS install a new steering column. Failure to follow this direction can result in steering column failure.”
It said a new adaptive energy absorption steering column should be installed if the:
-
- Steering wheel is bent, loose, or damaged;
- “Steering column functionality is binding, bent, or sticking;
- Steering column bearings display brinelling or other damage; or
- “Steering shaft is bent, loose, or damaged.”
It should also be replaced if any abnormal steering column movement is detected, On Target said.
I-CAR noted in a December 2019 article how steering columns have advanced from basic shafts to a “highly complex” vehicle part.
“Today’s steering columns have steering angle sensors, air bags, clock springs, heated steering wheels, and controls for multiple systems,” it said.
I-CAR said that while collapsible steering columns have been mandatory in the U.S. since the late 1960s, they were originally designed to do so through mechanical designs. Newer steering columns can now collapse from the force of the driver hitting the air bag, it added.
“In the event that the driver impacts the steering wheel in a collision, the steering column is designed to shorten,” I-CAR said. “Some designs use a mechanical ‘pin’ that will shear off with a specific amount of force, or a piece of metal that will deform in a controlled manner. Other vehicles have columns which use a pyrotechnic device to release a mechanism, allowing the steering column to lessen in length and absorb energy from the impact.”
Following a collision, steering column inspections are mandatory by many OEMs, I-CAR said, adding that other automakers require the columns to be replaced after the energy absorbing mechanism has been used.
Repairs are advised to refer to service manuals when repairing vehicles equipped with such steering columns.
“Due to the complexity of the system, the functions may be computer controlled,” I-Car said. “This also means that diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) may be set if there are any malfunctions. A scan tool may be required to pull these trouble codes and diagnose any issues.”
SRS component descriptions
This On Target edition also included some additional SRS-related component descriptions and definitions, which it said can be found in Ford’s official workshop manual.
This includes the seatbelt retractor and pretensioner, “a pyrotechnic device that removes excess webbing slack from the seatbelts when deployed.”
“The retractor and pretensioner are serviced together with the front row outboard seatbelt assembly,” On Target said.
Those concerned about the seatbelt retraction for function should refer to Section 501-20A’s guidance on seatbelt systems’ diagnosis and testing. To diagnose DTCs, they should refer to Section 101-20B, which covers supplemental restraint systems’ diagnosis and testing, On Target said.
On Target also shared descriptions of its:
-
- Side air curtain, meant to protect a person’s head and upper body during collisions;
- Side air bag, to protect an occupant’s torso used in conjunction with the side air curtain;
- Clockspring, which allows for continuous electrical connects between the driver’s side air bag and restraints control manual (RCM); and the
- Battery energy control module B (EPMB), which supplies system voltage to the RCM.
“The BECMB requires programmable module installation (PMI) when being replaced. Refer to the diagnostic scan tool instructions to carry out PMI,” On Target said, later adding: “The RCM requires PMI when being replaced. Refer to the diagnostic scan tool instructions to carry out PMI.”
It said more details on SRS-related repairs from Ford’s workshop manual will be made available in future volumes.
Front door sensor
In the current edition, On Target also began a new series that examines the right way to properly remove impact sensors on the Ford Bronco, this time zeroing in on front door side-impact sensors.

Collision repairs should start off by referring to health and safety warning in its workshop manual’s Section 100-00, it said. From there, they should depower the SRS while referring to the manual’s Section 501-05 and then remove the front door side-impact sensor.
To remove the sensor, they should first disconnect the electrical connector and then remove the bolts, On Target said. It added that to install a new sensor, repairers should reverse the removal procedure steps.
More information can be found online through the OEM’s FordCrashParts website.
Images
Featured image courtesy of Vera Tikhonova/iStock
Illustrations courtesy of Ford
